APM is commonly used to describe two different practices: application performance management and application performance monitoring. While seemingly almost identical, these terms mean—and can lead to—two different things.
In short, application performance management is a subset of digital experience monitoring (DEM), while application performance monitoring has a narrower scope of a specific application’s functionality. Both involve identifying when an application is up and fully functioning, so what’s the difference?
Let’s start by zeroing in on our definitions of APM.
What Is Application Performance Monitoring?
Application performance monitoring examines the components and/or infrastructure of a given application. This is how Gartner defines application performance monitoring:
“One or more software and hardware components that facilitate monitoring to meet five main functional dimensions: end-user experience monitoring (EUM), runtime application architecture discovery modeling and display, user-defined transaction profiling, component deep-dive monitoring in application context, and analytics.”
This monitoring process involves a detailed analysis of the application stack itself. From here, the tool can monitor how well the application is functioning in each step or process (also known as a trace or transaction) the application goes through. Application performance monitoring can identify where specifically an application is failing.
What Is Application Performance Management?
Application performance management provides an overall picture of a software environment with a greater focus on resource utilization. It involves more awareness of the end user and their interaction with the application.
Application performance management helps IT spot application performance issues and identify correlations with the performance of other software and hardware in the environment. This approach is valuable for IT departments and business leaders wanting to understand which applications are necessary for end users to do their jobs as well as to what extent application performance problems are hindering productivity.
Three Ways to Spot the Difference Between APM Tools
While management somewhat encompasses monitoring, they have their clear differences. With these concepts in mind, there are three main differences between application performance monitoring and application performance management.
1. One Versus All
Application performance monitoring is monitoring each step within a specific application. An application performance monitoring tool can be used to diagnose code-level problems within an application. Due to its lack of scalability, often it’s not practical to have an application performance monitoring tool monitoring all applications enterprise-wide.
In contrast, application performance management is looking at the whole scope of all applications for each end user. An application performance management tool can provide insight into which applications may require more optimization than others.
Check out this short demo video to see application performance management in action.
2. Differences in Data
The data collected between the two APM methods varies due to the difference in end goals. Application performance management has an overall scope of data. Since this method is focused on user interaction with the application, it involves looking at metrics such as CPU consumption or memory usage. Due to its wide scope of data, application performance management helps identify the root cause of the impact an end user may be experiencing (for example, an application could be consuming one too many resources).
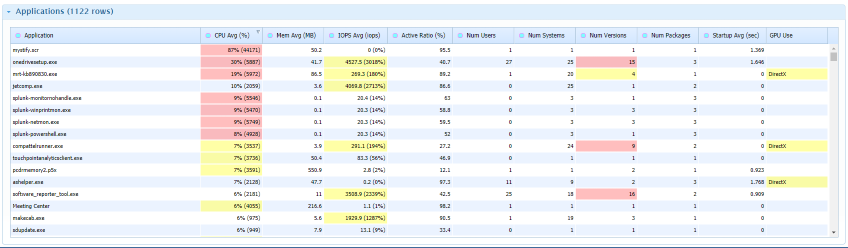
SysTrack analyzes many key metrics for each application, allowing IT to see what experience is like at the endpoint. Beyond transaction data, these KPIs assist in faster root cause analysis and issue remediation.
Application performance monitoring collects time-oriented data. An application performance monitoring tool analyzes each step of the application running and sees how long it takes to move on to the next step and compares that against what is expected. If the problem originates from the application itself, then an application monitoring tool can go in and pinpoint where it may be not fully functioning. This style of APM is often used by developers to troubleshoot code-level application errors.
3. End Goal
Application performance management is directly correlated with the endpoint through real-user monitoring. It involves being aware of the consumption of resources for each application to provide an overall picture of an end user’s experience. It also includes understanding how an end user might interact with an application. Application performance management goes beyond the scope of how a specific application is functioning on its own; it connects to a higher level of how all applications are running on a system together and how the end user is interacting with them. Therefore, an application performance management tool can provide context to why an end user may be experiencing impact.
Application performance monitoring is purely focused on how well one specific application is performing. If the application is passing the time thresholds that it should, then it meets the criteria and end goal. It can be assumed that if the application itself is running through its application stack in the appropriate time, then the user using it will theoretically have a high productivity. Therefore, an application performance monitoring tool can tell you that an application is moving a little slower between processes.
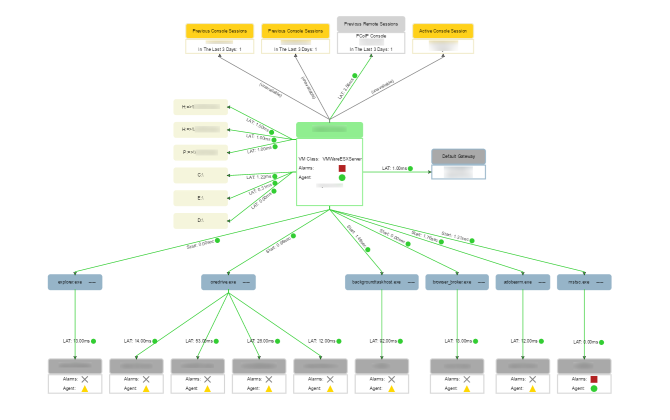
SysTrack can track application dependencies to identify which components may need to be looked at.
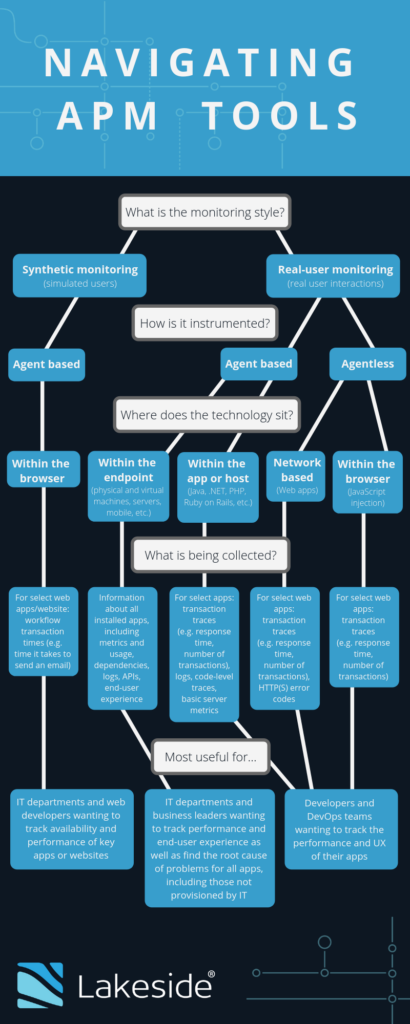
Not Sure What Kind of APM You’re Looking For? Use This Flow Chart
Navigating the tangled web of APM tools can be confusing, even if you’ve nailed down the differences between application performance monitoring and application performance management. Within these categories, there are still many differences in terms of how these tools are instrumented, what kind of data they collect, and who they’re designed for.
This handy flow chart breaks APM down even further to help you understand what type of APM solution best suits your needs.
About SysTrack
SysTrack is a digital experience monitoring solution that helps perform application performance management by providing greater visibility into endpoint performance and end-user experience. As displayed above, SysTrack can monitor various metrics associated with each application across an enterprise to help get to root cause quicker and optimize applications. It also provides insight into application dependencies that can help an IT admin identify why an application may not be working.
While SysTrack is not an application performance monitoring tool, it can be used alongside one to provide a complete view of how well an application is functioning independently and with other apps in the environment.
Want to learn more? Request a demo of SysTrack!
Subscribe to Lakeside Updates
Receive product updates, DEX news, and more



